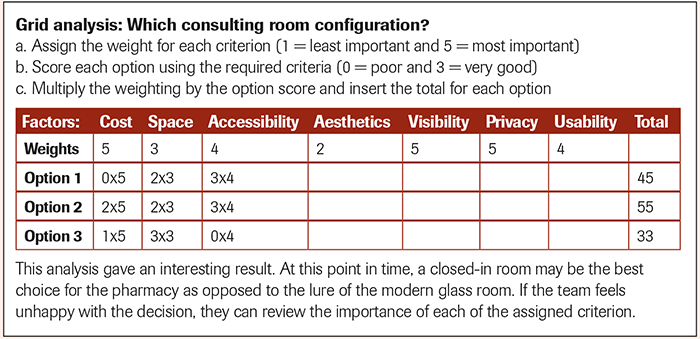
Grid analysis
Grid analysis, also referred to as 'decision matrix analysis', is most effective when there are a number of good alternatives and many factors to take into account.
- List all options and factors that are important for making the decision
- Arrange options as the row labels, and factors as the column headings (see figure 2)
- Work out relative importance of the factors in your decision
- Score each option from 0 (poor) to 3 (very good)
- Multiply scores by the values for your relative importance
- Add up weighted scores for your options. The option that scores the highest wins.
In the example below, the problem is defined as a deficient consultation room to deliver modern healthcare services.
Option 1 €“ one glass-panelled consulting room, sized 1m x 1.5m, on the ground floor
Option 2 €“ one closed-in room with a glass door, on ground floor and sized1m x 1.5m
Option 3 €“ two consulting rooms on the first floor, each of 2m x 3m.
When the relative importance of each of the criteria is weighted (below), there was a surprising result.