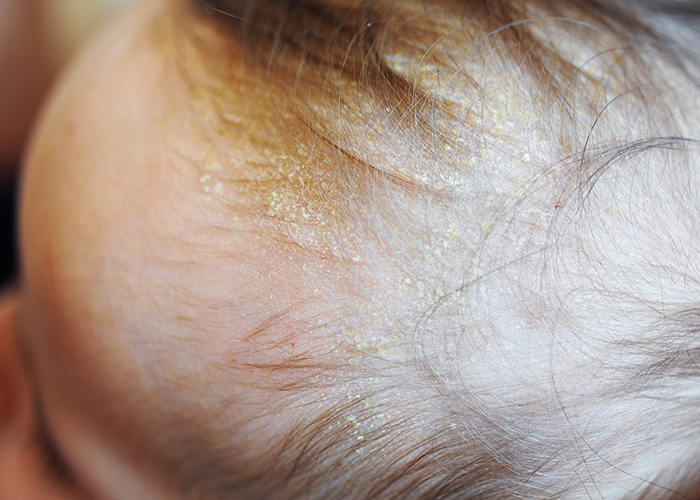
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is a common inflammatory skin condition that presents as mildly itchy, red, scaly patches in areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, nasolabial folds, ears, eyebrows, chest, flexures and skin folds.
Dandruff is thought to be a mild non-inflammatory form of seborrhoeic dermatitis and cradle cap in infants is also a form of the condition.
The exact cause of it is not known but treatment to reduce the number of Malassezia yeasts improves the condition.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis affecting the scalp and beard can be treated with regular use of ketoconazole or selenium sulphide shampoos. If these are not appropriate or acceptable then other medicated shampoos such as zinc pyrithione, coal tar or salicylic acid can be used.
For seborrhoeic dermatitis affecting the face and body, ketoconazole 2% cream (POM) once or twice a day, or another imidazole cream (clotrimazole or miconazole) for at least four weeks, is recommended. An antifungal shampoo such as ketoconazole 2% (POM) can be used as a body wash. Mild topical corticosteroids may be needed short term. It should be noted that it is safe to apply hydrocortisone 0.5% or 1% to the face, although the OTC product may not be supplied for this area as the SPC says that the product should not be used on the eyes or face.