Hypertension should be suspected if a person’s clinic blood pressure is 140/90mmHg or higher.
A patient’s blood pressure should be measured in both arms and where the difference in readings between arms is more than 20mmHg, the measurement should be repeated. If the difference in readings between arms remains more than 20mmHg a second time, the arm with the higher reading should be used to take subsequent measurements.
NICE guidelines state that the diagnosis should be confirmed with ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) or home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) if ABPM is not tolerated. ABPM allows blood pressure to be measured many times throughout the day and best practice dictates that at least two measurements are taken every hour during waking hours with the average of at least 14 readings recorded.
Home blood pressure monitoring is the alternative and patients should record their blood pressure twice a day (morning and evening) by taking two consecutive readings at least one minute apart while sitting down. Measurements should be taken over seven days (or at least four days) with the first day’s results discarded and the average value taken for the other measurements.
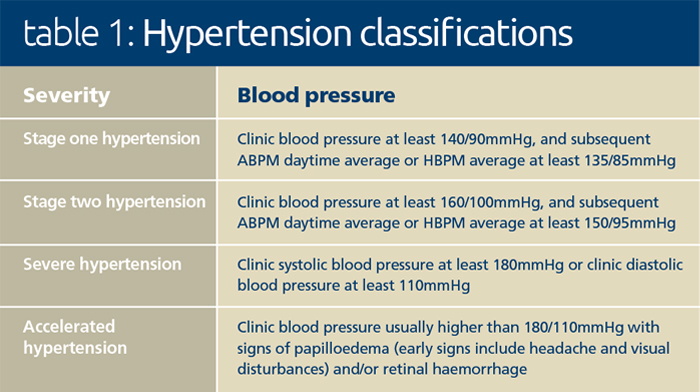
Hypertension is classified according to severity, as seen in table 1 below.